In this chapter we highlight the fundamentals of link building including what it is, why it's important and how to build links in a Google-friendly way.
In this chapter, we will focus on the basics of link building before taking a look at why you should spend time on it if you’re doing SEO for your site, and how it affects your site’s performance in the search results.
What Is Link Building?
Simply put, link building is the processing of securing hyperlinks (or backlinks) from external websites to your own. The idea here is to capitalise on the fact that search engines use links to navigate and crawl the web. Link building (often referred to as off-page SEO), is one of the most important factors when it comes to SEO and there are several techniques SEOs employ in order to secure links for their website.
Why Is Link Building Important?
Links represent the connections you make with other entities online, and they are a huge part of how Google decides what authority your site has compared to all the others that exist in the same niche.
Having great backlinks also gets you:
Referral Traffic – by mentioning you as a source of information, people will click on the link and visit your site in order to find out more.
Higher Authority – what does having authority mean? If you look in the dictionary, you’ll see that a person who has authority is “a person with extensive or specialized knowledge about a subject: an expert” – in this case, each link you get will confirm that you are a good source to go to for that type of information. The more good quality websites say that you are an authority on the subject, the more trustworthy you will become in your field.
Naturally, the more authoritative the site you’re getting backlinks from, the more authority they can transfer on to you. This is why targeting great quality sites for outreach is so important.
PageRank – PageRank is an original algorithm used by Google in order to rank pages, and to state what the importance of a specific page is when compared to others. The name of this algorithm actually refers to one of Google’s founders – Larry Page. Not a web page.
Although we still use the term PageRank, the fact is that Google now uses a complex network of algorithms in order to rank a website’s importance. These algorithms’ goal is to make the perfect match between user intent and what page best fits that intent.
It’s all about what the user needs. Links embedded in specific types of content will add to your site’s PageRank, and affect the complex system of how search results are managed.
PageRank is calculated on a page by page basis, NOT by domain authority.
What Makes a Link “Good”?
Follow vs Nofollow – before we get any further, let’s talk about the very basics of link anatomy.
Below, is an example of how a hyperlink is coded in its most basic form on a web page using HTML.
<a href=”https://susodigital.com/”> SUSO Digital </a>
Open Link Tag: Referred to as an “anchor” tag, this tells the search engine that there will be a link to another resource.
Link Resource Location: The “href” property stands for “hyperlink referral” and the text inside the quotation marks serves as the address that the link is pointing towards. This can be the address of another web page, image or a file.
Anchor Text: This is the clickable text that the user is able to see on the web page. When clicked, the user is directed to the Link Resource Location
Close Link Tag: This tells the search engines that the link has been closed.
When it comes to SEO, we have seen in previous modules that there are two types of links that instruct the search engine on how to treat each link, they are: “dofollow” and “nofollow”.
If there is a “rel=nofollow” tag at the end of a link, it means that the link is not passing on any authority and as a result offers no SEO value.
<a href=”https://susodigital.com/” rel="nofollow"> SUSO Digital </a>
You can check the code in a link simply by left clicking on the link and seeing what the code is.
A Little Link Building History

In the 90’s the internet was basically like the Wild West – whoever hacked, cheated and strong-armed their way to the top was noticed. This didn’t make for a good user experience, because it led to spam. A lot of spam.
A lot of businesses would stuff their sites so full of keywords that it would render them unreadable. Practices like hidden links, invisible text, link stuffing with spam.
Google started to introduce algorithm updates in order to combat spam and poor business practices. In other words, to make the internet browsable again. This is why black hat practices aren’t good and they never were – eventually, Google is going to shut it down.
rel=”nofollow” – In 2005, Google introduced the “nofollow” tag in order to further cut down on link building spam. SEO started to become more user focused and content friendly – Google was winning the quality game. The “nofollow” tag meant that you couldn’t spam places like forums and comment sections with links anymore.
rel=”sponsored” – Similarly, paid links are marked as rel=”sponsored”. This is so it’s clearly marked who paid for a link and that it’s a “sponsored post” – it won’t pass along the same kind of authority.
rel=”ugc” – Another tag to be on the lookout for is the “rel=ugc” – here, links that are made in user generated content can be marked. Sometimes, if the contributor is especially valuable and a website wants to be associated with him or her and pass the link juice along, they will remove this tag. This is why building solid and valuable relationships can pay off. It’s worth pointing out that it’s not about every content created by users, but more about the comments or reviews in places like product pages.
Every once in a while, someone will say that link building won’t matter soon – but judging by the trends that have been happening in every algorithm update that’s not the case – rather, Google is only getting better at recognizing useful links that give value and improve user experience. It’s only natural that these links would have a hand in improving the brand’s authority.
According to Search Engine Land, links and content are still some of the most important signals for ranking a page. While the way they’re being taken into consideration is becoming stricter, concentrating on getting high-quality links is a great incentive for improving the overall quality of content on the web.
Link Building Strategies
You don’t have to start from scratch when you start prospecting. There are some tried and proven-to-work strategies that you can employ in order to get links. Remember that the SEO landscape can change fast, and strategies that were rewarding and effective some years ago can potentially be problematic and get you into Google jail today.
Before we start on strategies, we’d like to remind you of some link building strategies that you should avoid, these are often referred to as “black hat” techniques because they do not follow Google’s guidelines when it comes to link building.
Link Building Strategies to Avoid
PBNs
A PBN is a Private Blog Network – this can be a network of websites or blogs (and directories) that make their money exclusively from selling links. Their websites will often be a collection of badly written content, and all niches jammed together into a topic salad. Poor content generates poor traffic. Their menu will most likely be made up of genres like: Self care, tech, pop culture, health, gadgets, exercise, politics, travel, beauty – with cannabis articles thrown into random places just for fun.
Sometimes, they will be better designed and niche specific – only after you submit a pitch and get back the answer will you smell something fishy going on – you will get a list of anywhere from 10 to 100 “affiliated” websites that you can also post on – for a fee. Some of these sites might look very tempting – but don’t do it! It might not get you a penalty but it will simply be an “ignored” link. Why waste the time and effort?
Over-Optimised Link Building
Too much keyword optimisation can also be a bad thing – in 2020 there are a lot of SEO experts that say “let the people choose” – meaning letting the prospects choose a natural sounding anchor will be better for you in the long run.
The addition of BERT has helped Google understand language better, and process people’s intent – and what’s most important, understand the context behind a word. As understanding search queries becomes more organic, so will the understanding of the context of anchor texts. In this new world, optimized anchors will become painfully obvious, and it does not look like a natural link profile.
Write For Us
Sometimes, websites will go out of their way to invite site owners to provide their own content in exchange for a hyperlink. Most of the time, it means they are a PBN or get a part of their income from selling links. This is also a big “no” because it violates Google’s guidelines on acquiring links “naturally”.
Recommended Link Building Strategies
Blogger Outreach
Outreaching to genuine bloggers that have experience and authority in their niche. You can build a relationship with them and put together content that really ranks. We will go into more detail on how to conduct blogger outreach later on in this module.
Broken Link Building
Searching great quality sites for broken links – that used to point to other niche pages but no longer exist. You can point out the broken link in your email, and offer a page with similar content on your site – hopefully content that is up to date and well written. It’s good to look for links that have been neglected by your competitors.
As you can see here, Ahrefs.com even has a free tool you can use to monitor the broken links on your own site.
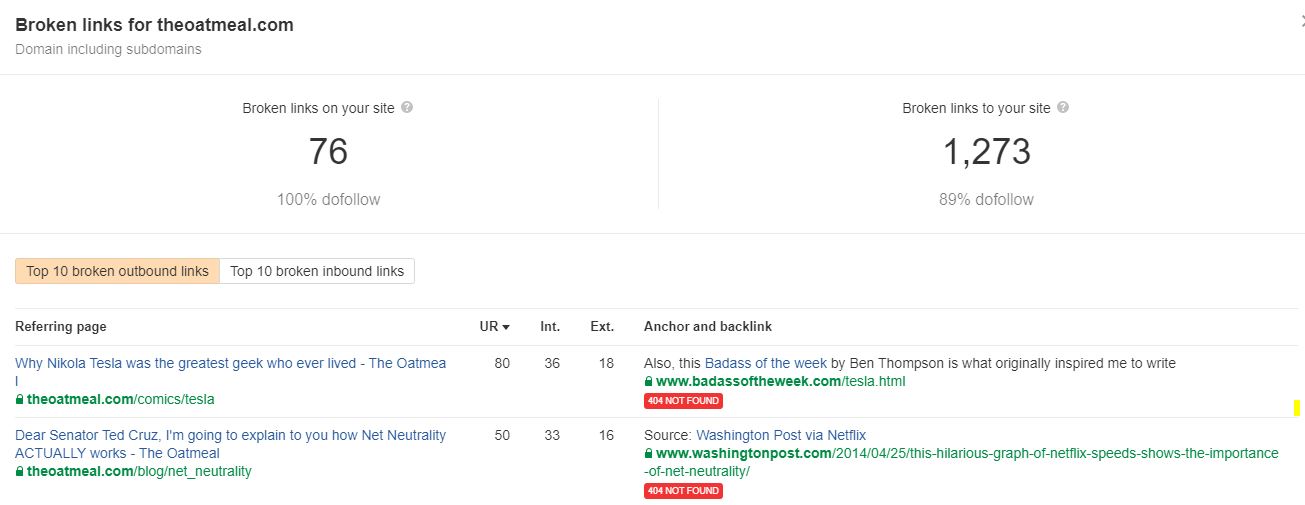
You can also find what external backlinks point to any broken pages on your website. Fixing those will help you a lot.
Finding Broken Backlinks
Enter your website address into Ahrefs, and click on the “Broken” option under “Backlinks” in the left hand side.

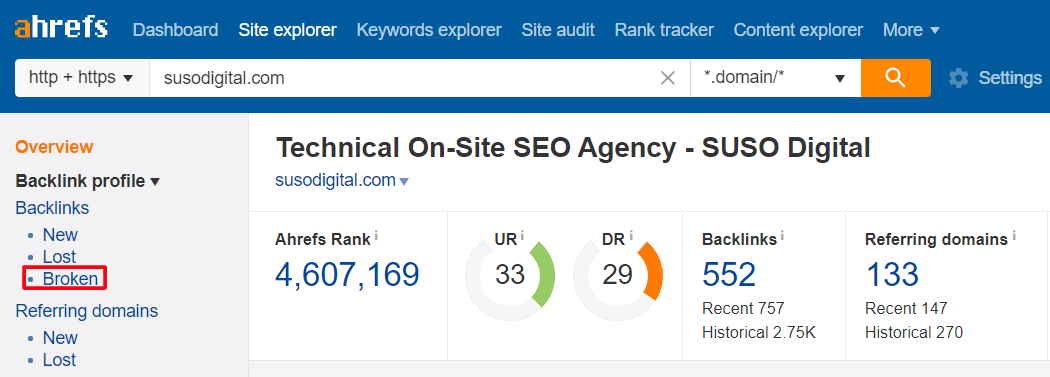
To find a competitor’s broken backlinks, do the same but with your competitor’s address.
If you’re a bakery, you may see that there are a lot of links pointing to a competitor’s broken chocolate chip cookie recipe. Compile a list of those websites and reach out to them with a working page that contains a better recipe with a vegan option – you might have just earned yourself a lot of backlinks AND organic traffic.
Brand Mentions
Is your brand already pretty well known in your niche or locality?
Take a look if there are people already talking about you – mentioning your products or services. You can find who is mentioning you by using the “Content Explorer”.
Make a list of your branded products or services, or if you’re a business owner – even your own name. Enter it into the content explorer, and you will have a list of places where it’s mentioned – easy!
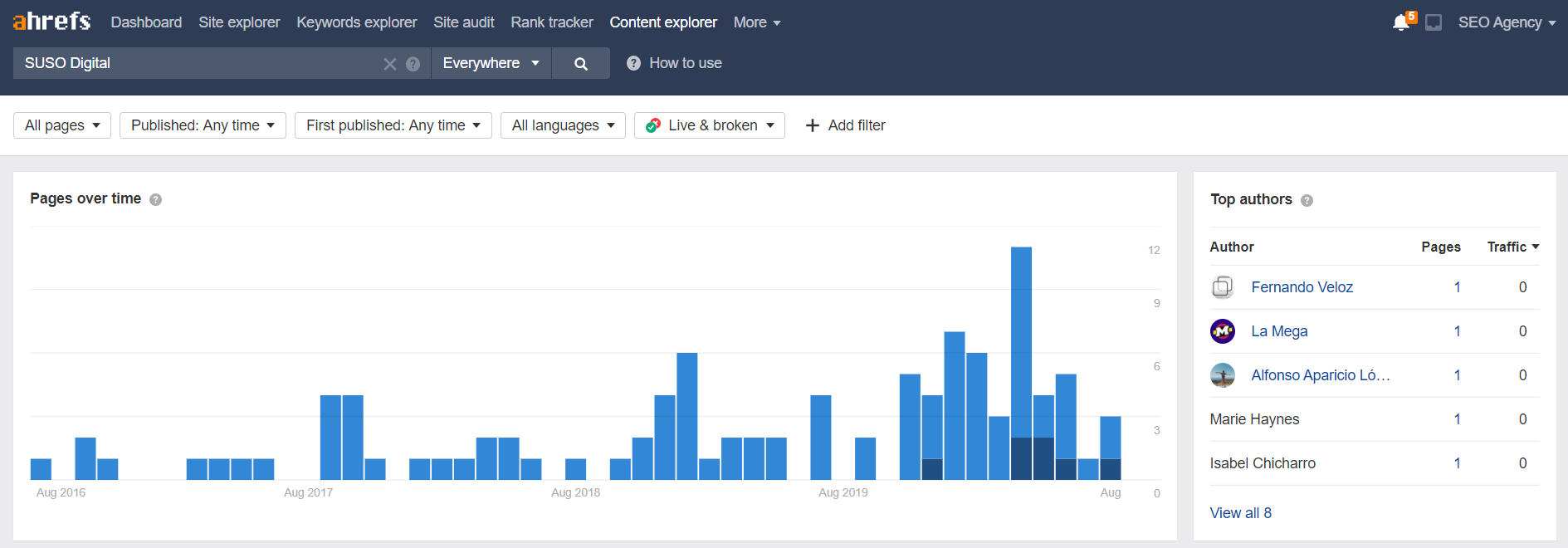
*Tip – it’s a good idea to use a quality filter, so you only see pages that have high authority.
Here is the ABC of finding great opportunities for brand mentions:
- Make a list of products specific to your company. For example, a company like See’s Candies would look for the terms “See’s Candy” but chocolate truffles, See’s chocolate gift boxes, chocolate gift sets. Anything that they can think of that’s related to what they do.
- Don’t hesitate to use the name of business owners or partners. Whenever they’re mentioned online, their business can be too. This can earn you a lot of links quickly.
- Look for these terms in content explorer, making sure that you’re only looking for results that aren’t linked to your business:
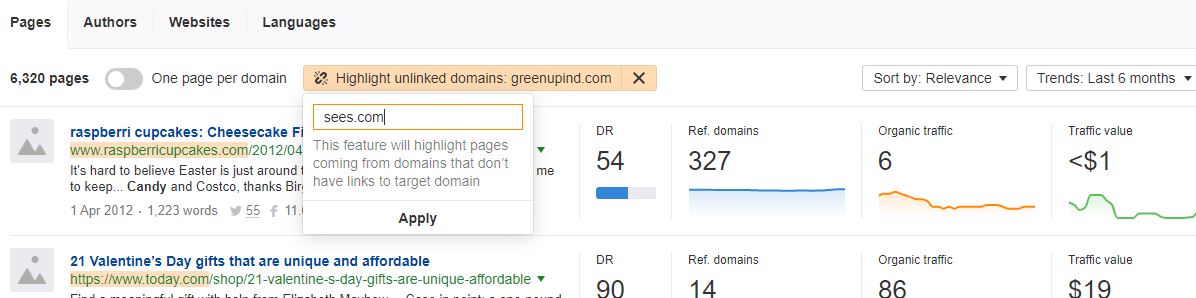
- Once you have built up a good list of these results, preferably on a spreadsheet, you can plan an email campaign to the publishers of the articles that mention your brand or product. This is easier than a cold email, since they are already mentioning you or your products, and most publishers will be happy to link in this case.
Topic Mention/Resource Sharing
You can use the same strategy as above if you have a valuable resource that bloggers can use to support their article. For example, if you’re a garden supply store and you have a tool like a planting and harvest calculator, you can look for articles on planting and harvesting – reach out to them and tell them all about your tool. It’s not spammy, but helpful and insightful, and this is how today’s SEO should be done.
Competitor Analysis
Sometimes, your competitors are a lot better than you at targeting the right websites. Chances are, that these websites will also give you a link if you approach them correctly.
The best tool for this is, again, Ahrefs. Other tools that can be helpful are the ones built especially for Outreach, like Pitchbox.
This takes some reverse engineering and seeing how your competitor got the link in the first place – did they write great content? Did they share an infographic? You can try to replicate this method for yourself.
Here are the competitors for See’s:
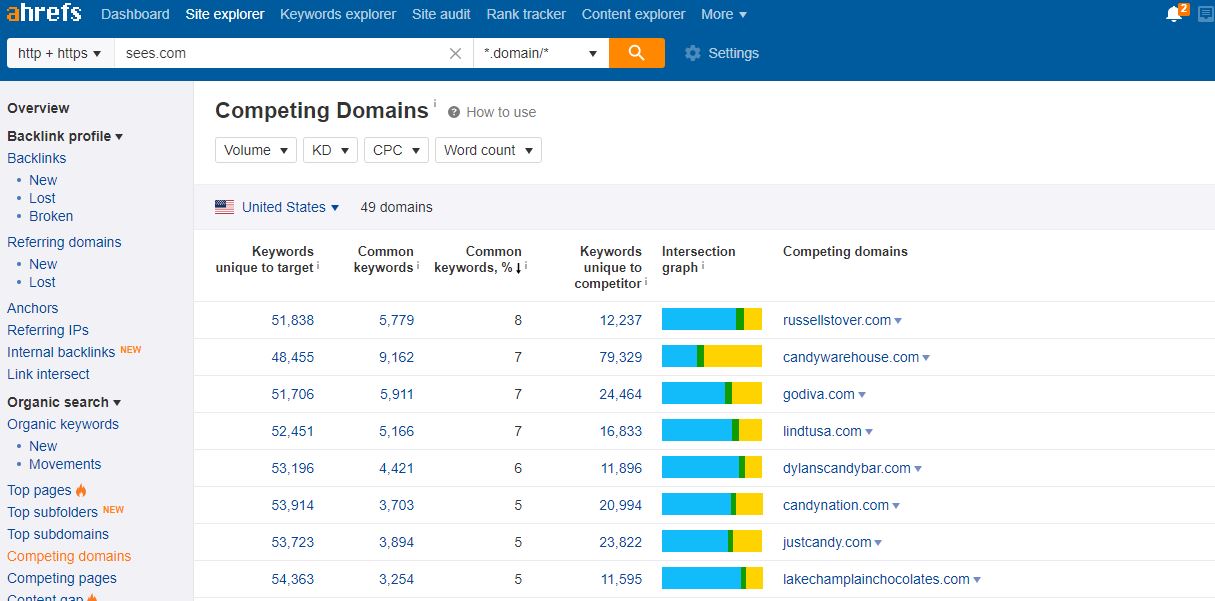
As you can see, there are a lot of them – each one of them has an amazing list of backlinks, if we only look. This is usually a goldmine of potential prospects, and if you’re doing it manually, it might take some time to filter. You should filter by:
- Tags
- Page authority