Find out how SUSO produces bespoke white-labelled SEO health checks for our client’s websites to uncover common & critical issues holding them back from higher rankings.
How SUSO Produces White-labelled SEO Health Checks
Author: Hadi Waqar, SEO Analyst

Introduction
Hi, my name is Hadi, SEO Analyst at SUSO. One of my responsibilities includes health checking potential clients’ websites before their onboarding to identify how we can help them rank their website for important terms or regain the website’s lost rankings if it has been impacted by a Google algorithm update.
In this guide, I am going to show you how we produce our white-labelled SEO health checks. But first, let’s look at why doing such checks is important…
Importance of Performing SEO Health Checks
Performing regular SEO health checks is important as you’ll be able to find and fix issues while they’re still small.
A good interval for a regular SEO health check is every 3 months. For larger and high-traffic websites you should perform a regular health check every month.
Why We Produce White-labelled SEO Health Checks
As an outsource SEO agency, we work with a range of partners who white-label our services to their clients. Our partners use the bespoke SEO health check reports that we produce to initiate SEO conversations with the brands and organisations that they work with.
Here’s how performing a website health check is useful for our partners and their clients:
- Allows our partners to show their clients how they could benefit from SEO
- Provides a glimpse into some of the most pressing issues that the website has
- Allows us to highlight keywords that are important to our partners’ client’s business goals.
- We’re able to showcase the potential clients our expertise before their onboarding.
- Help potential clients allocate proper budget to the campaign in view of the issues highlighted during the early analysis.
Below are the most common SEO factors that I look at when performing an SEO health check.
Current Performance
Google Core Algorithm Update
The first check I make is to see if the website’s SEO performance has been affected by a Google Core Algorithm update. With Google’s algorithm updates rolling out on a regular basis, it’s important for me to be able to understand and identify these in order to future proof our client’s websites and reduce the risk of them losing organic traffic and search engine visibility.
Using Ahrefs’ Organic traffic report, look out for periods where your website’s organic search traffic has seen a sharp rise or drop. Here’s an example of a website that was significantly affected by the Google “Medic” update which rolled out in August 2018 and largely focused on the Expertise-Authoritativeness-Trustworthiness of websites.
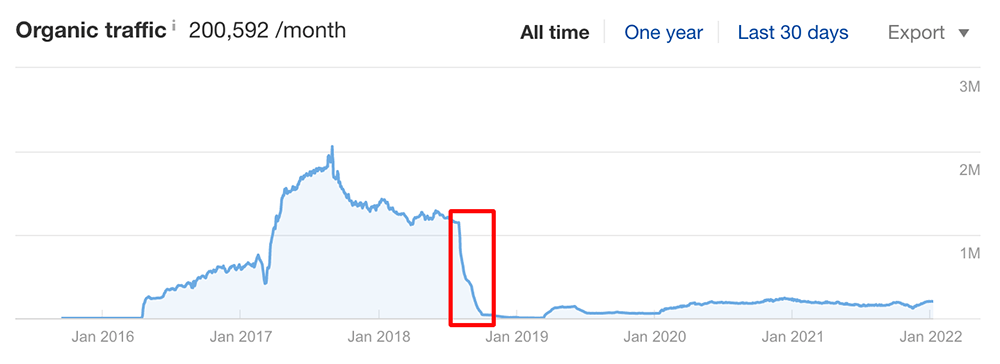
Being able to identify which algorithm update affected your website helps you understand why your website’s SEO performance may have dropped and in turn inform the strategy for your website’s recovery.
Keyword Visibility
I use Ahrefs’ Organic keywords report to look at the website’s keyword visibility in the top 100 positions of the search results.
This allows you to quickly see whether the number of keywords that you’re ranking for has grown or declined over time.
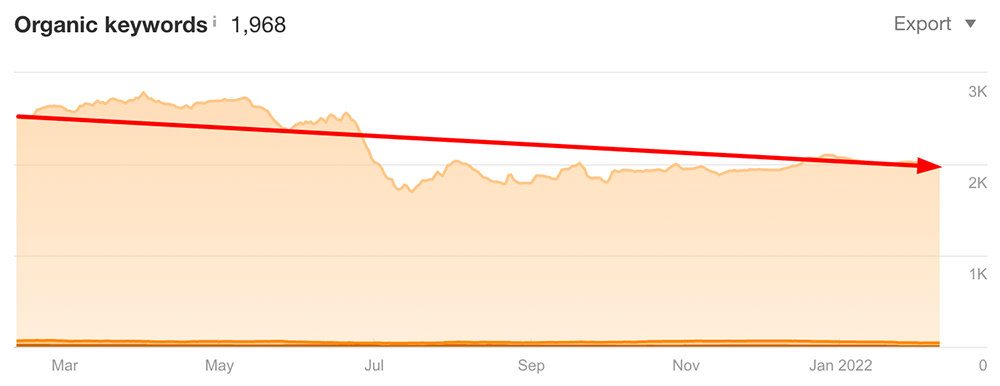
Image: the website lost 20% of its overall keywords ranking over a year
You should also look at the performance of keywords ranking in the top 10 and 3 positions.
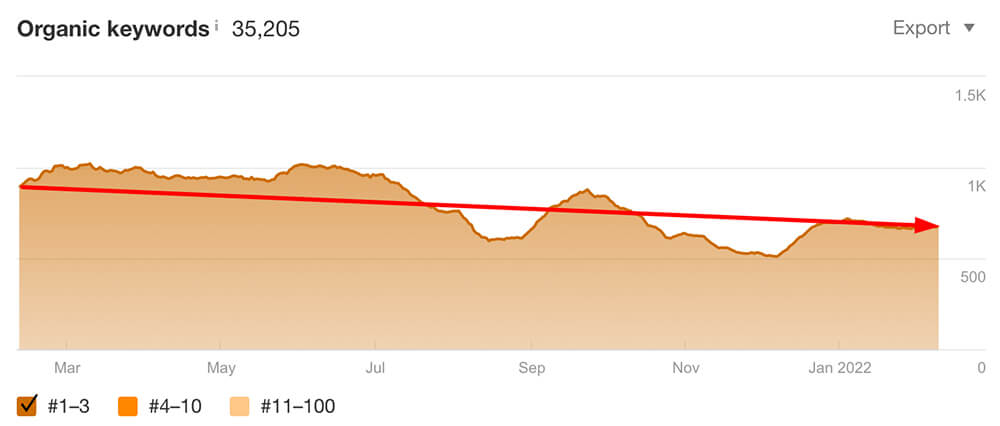
Image: Website lost 25% of its top 3 keywords ranking over the past year
These are especially important as they generate the majority of organic traffic towards your website.
Low Hanging Keyword Opportunities
Many websites will have keywords that are ranking just outside of the top 10 positions of the search results – these are considered “low hanging” keywords.
You can identify such keyword opportunities using Ahrefs’ Organic keyword tool:
- Filter by positions 11 – 20
- Filter by search volume (i.e. 100+)
- Select keywords that are important for ROI
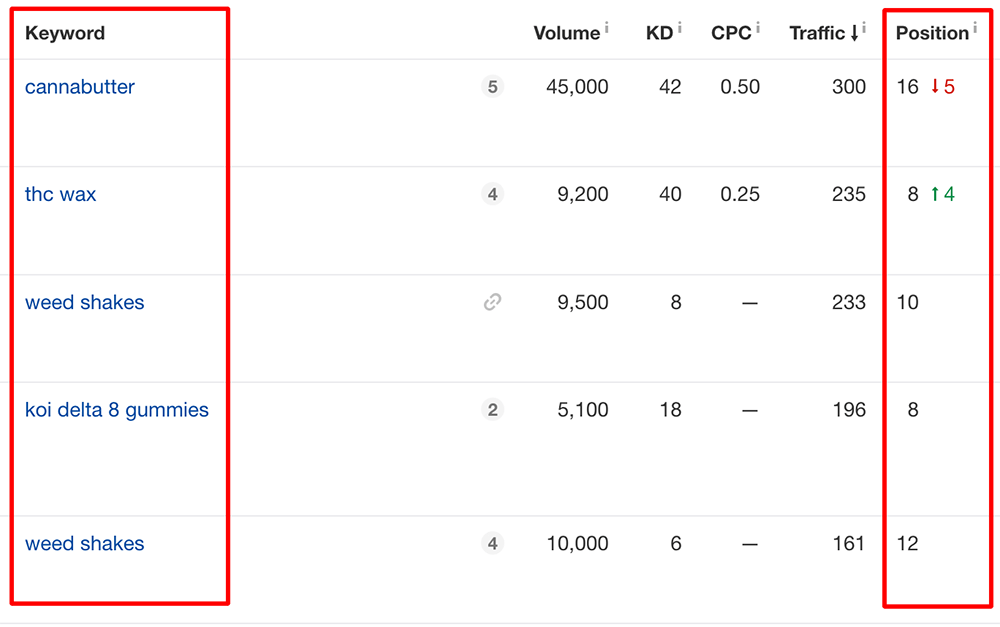
Image: Commercial Intent Keyword Opportunities for Potential CBD client
Looking at these keywords allows us to identify opportunities that present quick wins for our clients’ SEO growth.
Keyword Analysis
After getting an understanding of the website’s overall SEO performance, the next step in the process is to delve deeper into analysing why our potential client’s website isn’t ranking for a particular keyword.
This allows us to explain to our clients what factors are preventing their website from outranking the competition.
Below are just some of the elements to check:
Page Title
Do the top ranking competing pages have better-optimised page titles for the chosen keyword?
Page titles that are easy to read, include the core keyword that you want to rank for and are engaging result in better click-through rates.
Heading Optimisation
Are the headings on the page well optimised for the selected keyword?
For example, the H1 heading should summarise what the user will find on the web page as well as be optimised for the primary keyword that is being targeted.
Heading Structure
I also look at how the heading structure of the page compares against the top-ranking results.
Doing this highlights any content gaps: topics that the prospective client’s page may not have included, but the top ranking pages have included.
This helps to create a well-informed plan of which topics should be included within the content in order to rank for the target keyword.
Search Intent
In the next step, I look at a few core keywords to see if the page is satisfying the user search intent.
Common types of Search Intent include:
- Informational
- Commercial
- Navigational
- Transactional
Here I make use of Ahrefs “Keyword Explorer” to look at the top 10 ranking results for the keyword and compare the potential client page type against the top-ranking results.
This is one of the most common issues I come across with ecommerce websites where a potential client is targeting the “Product” page for a targeted term and Google is preferring to rank the “Category / Collections” page.
“Sherpa Jackets” is one example of a keyword where one of our potential clients was targeting the Product page and Google is preferring to rank Category or Affiliate (Top 10 Listicle) Post.
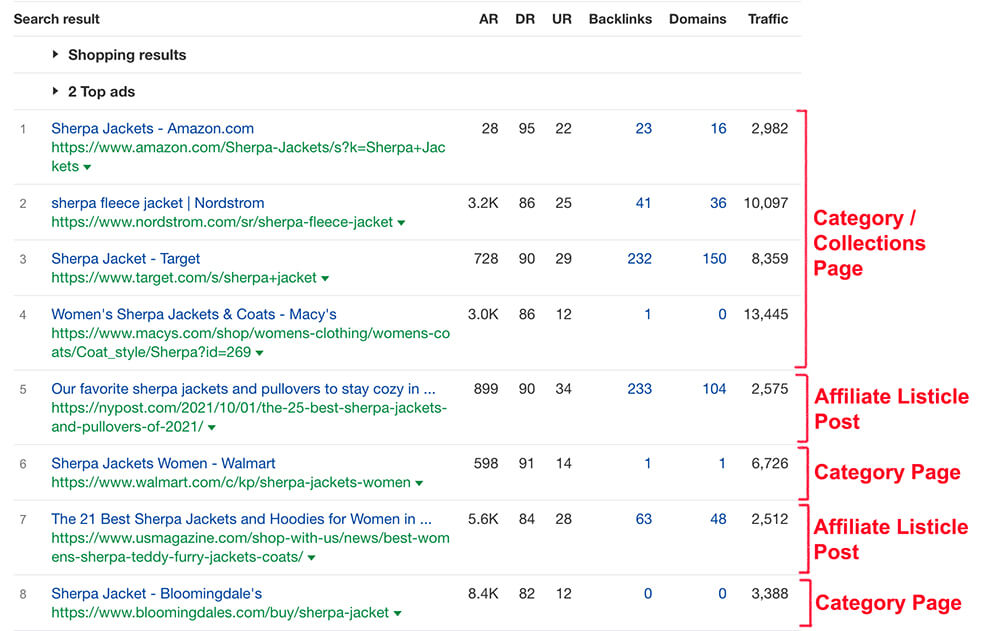
In order to succeed with SEO today each page of the website should satisfy search intent and provide value.
Keyword Cannibalisation
Keyword Cannibalisation is another common issue that prevents websites from ranking to their potential. This issue occurs when there are multiple pages from the same website trying to rank for the same keyword.
To check for cannibalisation, click on the Show History Chart icon on the right-hand side of each keyword present in the Organic keywords report on Ahrefs.

Here’s an example of what you need to look out for:
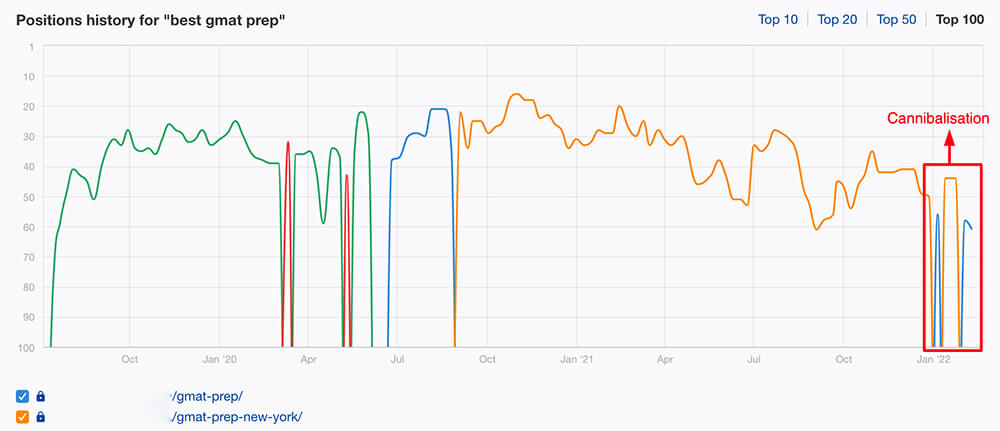
You can easily spot the cannibalisation as Google has switched between multiple pages (blue and orange lines) over a short period of time. Importantly, neither of the pages that Google has alternated between in the above example is ranking well.
There are several ways to combat keyword cannibalisation:
- a) identify and optimise the most relevant page
- b) de-optimise the least relevant page(s)
- c) add a canonical tag or 301 redirect from the least relevant page(s) to the most relevant page
- d) delete conflicting pages
- d) combine similar pages to create a single master page
Each case of cannibalisation warrants a unique strategy, i.e. some instances may require a simple 301 redirect whilst other more complicated situations, may require a combination of the solutions highlighted above.
Link Profile
A core component of SEO is link building. Performing a health check on our client’s websites is crucial as it helps inform how important the link building strategy will be for the website’s SEO campaign.
Authority & Trust
I compare the authority of the potential client’s ranking page for the selected keyword against that of the top ranking results. Here’s what I do:
- Go to Keyword Explorer in Ahrefs
- Enter the chosen keyword and make sure the correct Location is selected.
- Scroll down until you find the Top Search Results section.
- Compare the Domain Rank (DR) & Number of Referring Domains (RD) that the top competing pages have against the potential client’s core page.
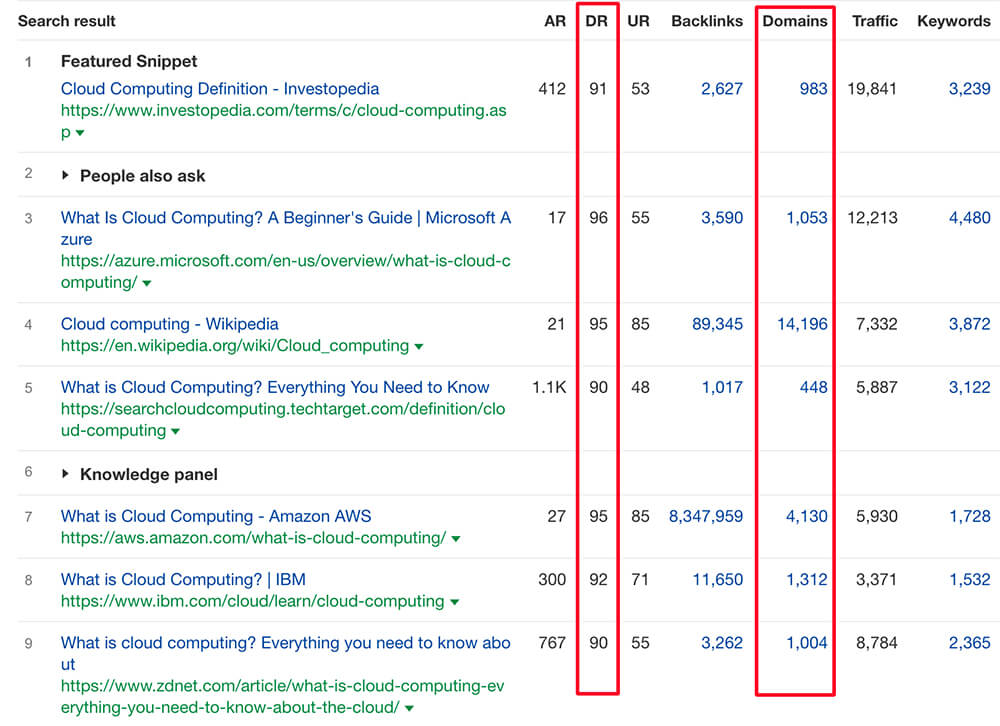
Image: DR & RD of top-ranking results for keyword “cloud computing”
Although Ahrefs Domain Rating (DR) score and the number of Referring Domains (RD) is by no means a definitive measure of a website’s authority – it does provide a good indication as to where the website stands in relation to the competition.
For example, if the client’s website has a much lower Domain Rating than the competitors, it suggests that more focus is needed on building more authority towards their website with topically relevant backlinks.
Anchor Text Distribution & Referring Domains (RD)
I also look at the anchor text profile of the website to make sure that it has a natural distribution.
The anchors texts (textual element of a hyperlink) used to link to your website should be using a mixture of:
- Branded (i.e. Nike)
- Naked URL (i.e. nike.com)
- Keyword-rich
- Exact match (i.e. nike sweatshirt for men)
- Partial match (i.e. check out these sweatshirts)
- Topical (i.e. basketball)
- Generic (i.e. click here)
Sometimes competitors may create toxic links to trigger a manual links based Google penalty by manipulating the anchor texts used to link to your website.
Here’s an example of an anchor text profile that is over-optimised with too many targeted, exact match keyword anchors and unnatural anchors that simply have nothing to do with the website.
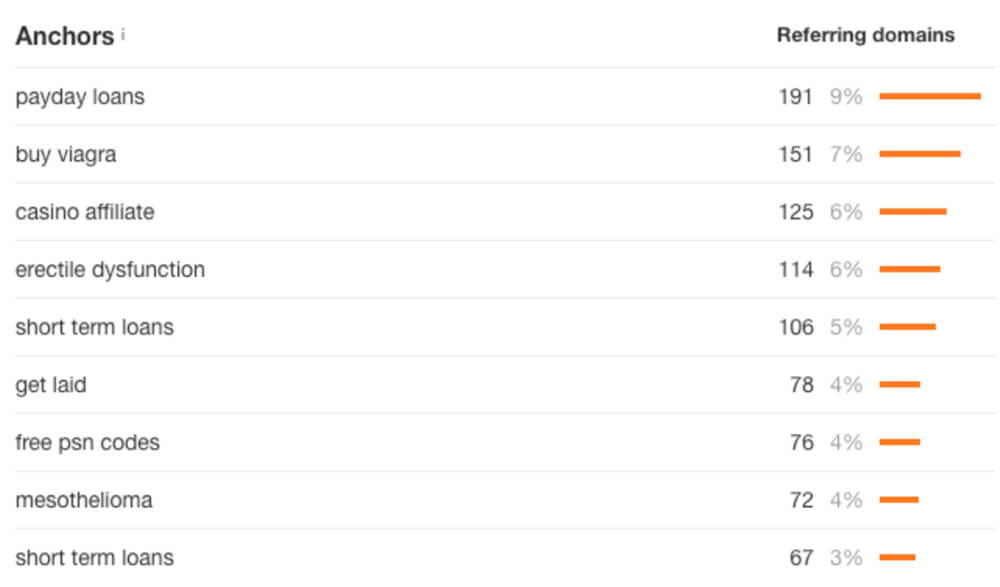
Another indicator of fowl play is if the number of Referring Domains (RD) has seen a significant spike in a short span of time.
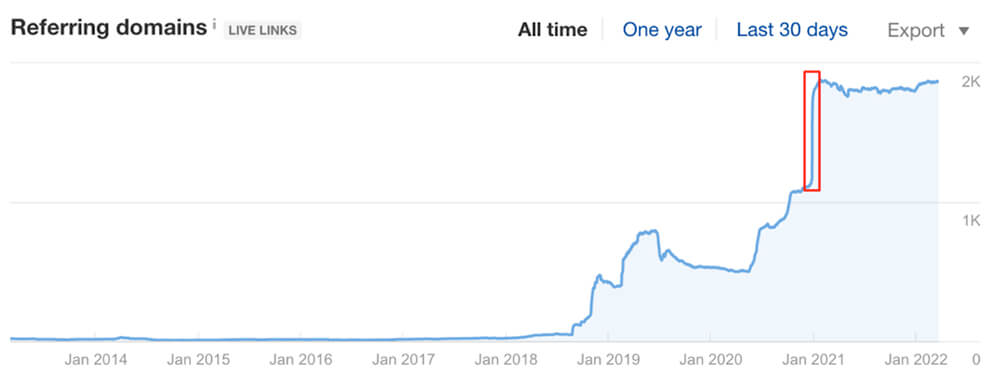
This gives us an early indication that we would need to perform a full backlink audit and manually analyse the individual links (and referring domains) to determine whether they are harmful or not.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO forms the foundation of any SEO campaign. This is all about making sure that the technical elements of your website are both Google and user-friendly. Below are examples of three technical SEO factors that I focus on when performing an SEO health on a website.
Structured Data
Even though structured data is not a direct ranking factor, it’s important to mark up your web pages with appropriate structured data because it:
- Increases your chances of appearing as a rich result (or featured snippet)
- Gets your brand in Google’s Knowledge Graph
- Helps Google understand exactly what is on the page
Here are some of the popular uses of schema:
- Organization – Used to describe an Organization (or business)
- People – Used to describe a person.
- Product – Used to describe any products that you may offer.
- Reviews – Used to describe a review of an item i.e. a restaurant, movie, or book.
- News Articles – Used to describe an article whose content reports news.
- Tickets – Used to describe a ticket to an event, a flight, a bus ride, etc.
- Events – Used to describe an event such as a concert, festival or lecture.
- Recipe – Used to describe a recipe
The most common missed optimization opportunity I came across websites is not using Organization markup on the homepage and Product markup on e-commerce Product pages.
Page Experience & Core Web Vitals
Google rolled out the Page Experience Update in June 2021 which
determines rankings by evaluating whether or not web pages deliver an enjoyable experience to searchers based on several page experience metrics that include:
- Mobile-Friendliness – are the web pages mobile-friendly?
- HTTPS – have the website been switched to HTTPS?
- Safe Browsing – do web pages contain any malicious content?
- No intrusive interstitials – are there any pop-ups that disrupt the user experience?
I check the Page Experience and Core Web Vitals score of either the homepage or one of the commercial intent pages of websites to determine whether this is a factor that may be contributing to a poor SEO performance.
This is because regardless of how well you optimise the content, if your page doesn’t provide a good user experience, your visitors are going to leave your website and visit a competitor instead.
Here are two tools that are great for measuring the performance of your website’s Page Experience:
Index Management & Crawl Budget
One of the most common issues websites face is having unwanted pages in Google’s index.
Googlebot has a limited amount of time that it can allocate to reviewing your site, which means it’s essential that the robots’ time is utilised efficiently.
Index management is about making sure that Google only crawls and indexes the most important pages on your website.
I’ve listed the most common types of pages that shouldn’t be indexed by Google:
- Empty categories on eCommerce stores
- eCommerce Sorting & Views (indexed URLs while sorting products by price, date, or popularity)
- /tag/, /author/ pages from your blog
- HTTP pages
Here’s an example of a website that has more than 12k HTTP pages indexed even though the website has an SSL certificate present.
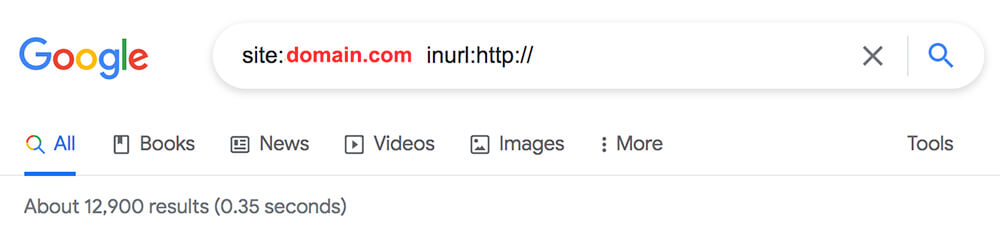
This creates unnecessary content duplication (because each of these HTTP pages will also have a corresponding HTTPS page that is identical) and wastes precious crawl budget (Googlebot could have spent its time crawling and indexing pages of higher value).
It’s important that you make it as easy as possible for Google to crawl the most important pages on the website and make sure robots’ time is utilised efficiently.
Conclusion
In this guide, I’ve shown you how we produce our white-labelled SEO health checks to help our partners initiate conversations about SEO with their clients by looking at the most common SEO issues that a website may face.
If you need help with launching an organic search campaign, want to safeguard your website against algorithm updates or want to find out more about our services and partnership opportunities, don’t hesitate to get in touch!
More articles
View more of our research.

Constructing An eCommerce Website for SEO
Find out how to construct an eCommerce website that is great for users and accessible for search engines.

Educating Clients on the Value of SEO: A Guide for Marketing Managers
Find out how marketing professionals can transform their clients' perception of SEO by educating them about the value that it can bring to their businesses.
